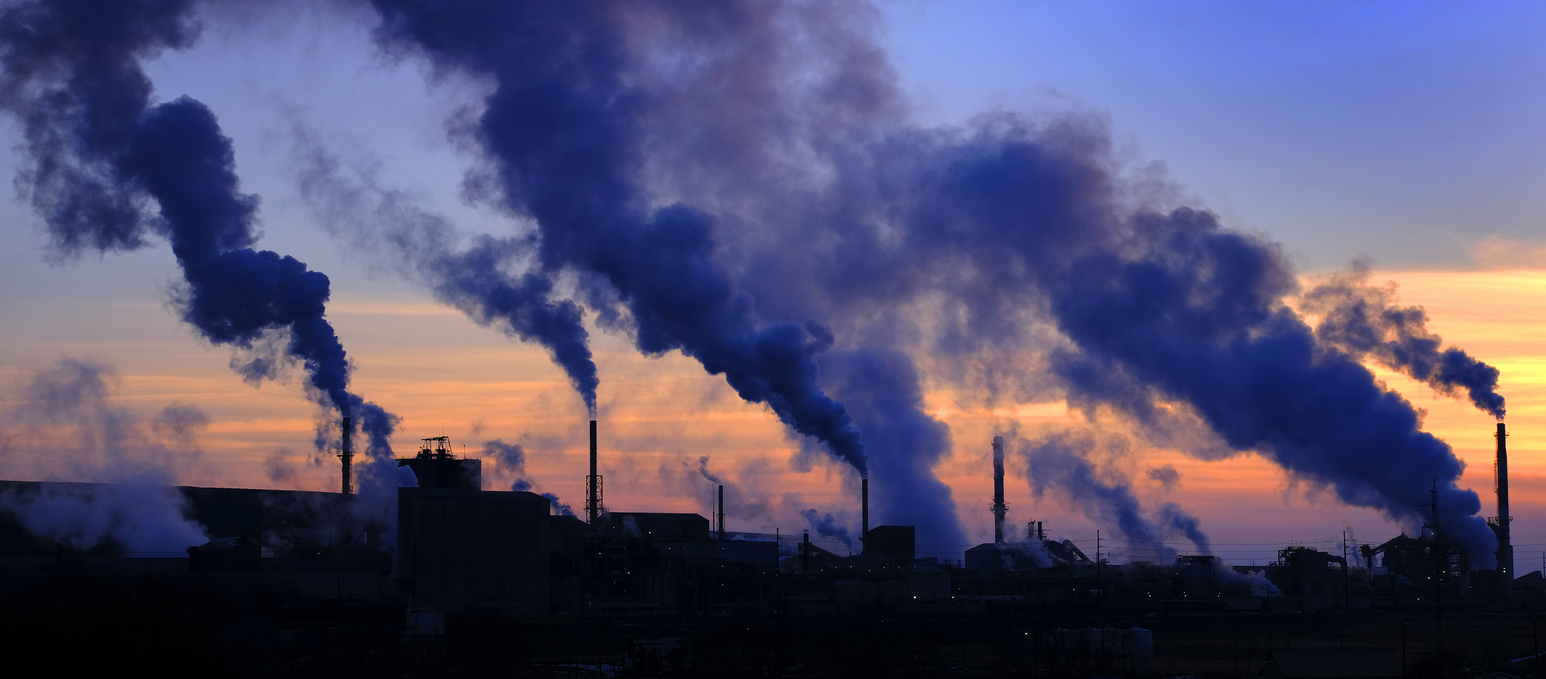
One of the most enduring claims about climate change looks at global warming cycles.
A widely repeated suggestion by climate sceptics online is that climate change observed in recent decades is part of a natural cycle of weather that is not linked to human causes.
Climate change is happening…. But it is a natural cycle that has nothing to do with human activity.
Social media claims
As part of our series, Scotland and the Climate Crisis, Ferret Fact Service looked at this claim and found it False.
Evidence
Climate cycles have been a focus for global warming sceptics for many years.
The claim that warming we are witnessing is part of a natural cycle of weather, rather than a result of human-caused climate change, has been repeated in various forms by politicians, social media influencers and climate sceptic groups.
How does the climate change naturally?
There have been several large changes in the earth’s climate throughout history.
These have been linked to a number of natural factors including changes in the sun, changes in the planet’s orbit and differences in carbon dioxide (CO2) levels.
As the sun is the earth’s source of energy, variations in solar activity have an effect on the global climate. Energy from the sun passes through space until it hits our atmosphere, where some of it is intercepted and reflected back, and some is absorbed.
However, this is not what drives temperature change on earth. There are variations in the energy output of the sun over time, but this has a very small impact on global temperatures. Notably, the rise in average global temperatures over the last 50 years has not coincided with an increase in energy received from the sun.
Changes in the planet’s orbit can also impact the climate. Serbian scientist Milutin Milankovitch suggested that changes in earth’s position relative to the sun could explain some of the long-term climate differences. This is because of slight differences to the amount of the sun’s energy that is absorbed.
These orbit changes are thought to be part of the reason that earth has shifted between glacial periods, where ice covers much of the northern hemisphere, and interglacial times where ice has been restricted to the poles.
Known as Milankovitch cycles, these occur between 23,000 and 110,000 years apart. They do not account for the rapid warming in the last century, and scientists observed that these cycles have not changed the amount of solar energy absorbed by earth over this period.
In fact, scientists believe Earth’s current positions within the Milankovitch cycles predict our planet should be cooling, not warming.
Volcano activity is regularly cited as a cause of climate change, due to the CO2 released into the atmosphere by eruptions. The CO2 released during eruptions is, in fact, much smaller than the amount of carbon humans release into the atmosphere every year. According to NASA, human activity emits the same amount of CO2 as the eruption of Mount St Helens every two and a half hours.
Scientists believe that major eruptions can actually cause short periods of cooling in temperature. Particles and other gases are thrown into the atmosphere, and effectively shield earth from some of the sun’s rays for a short time.
Crucial to the earth’s climate and temperature is El Niño and La Niña, which describe unpredictable cycles of warming and cooling of water in the Pacific ocean. They are part of a larger phenomenon called El Niño-southern oscillation (ENSO), which can affect global temperatures, but does not explain the consistent warming that we are experiencing in the 20th and 21st centuries.
How have global temperatures changed over time?
The Earth’s temperature has altered significantly through its history, with periods of warming and cooling having massive impacts on flora and fauna.
The last one million years has seen a number of ice ages, with glacial and interglacial periods taking about 100,000 years to cycle. The current period, stretching back a few thousand years, is interglacial, with earth’s temperature being fairly constant.
What impact have humans had on the climate?
While global temperatures have increased and decreased over long term periods, the warming experienced over the last century is unprecedented.
Burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil have increased the amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere.
When CO2 and other GHGs enter the atmosphere they increase the greenhouse effect. This is because they trap heat inside the Earth’s atmosphere, and lead to warming of its surface temperature. While greenhouse gases are natural, industrial activity from humans has raised CO2 levels by nearly 50 per cent since 1750.
The clearing of land for human purposes such as agriculture, industry or housing has also had an impact, reducing the natural ability of the earth to store carbon which can reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
One of the reasons we can tell that human activity is causing climate change is due to fingerprints that carbon emissions into the atmosphere leave. These help scientists to identify its source.
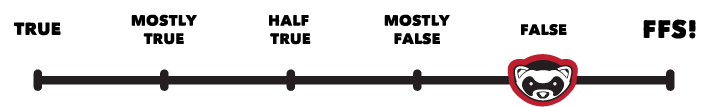
Ferret Fact Service verdict: False
Claims that climate change in recent decades is solely a result of natural variations in weather and ‘climate cycles’ is incorrect. Scientists agree that while various natural effects can impact the climate, the current warming is a direct result of greenhouse gases put into the atmosphere through human activity.